Clinical Research Translation for Global Access to Medical Innovations
Clinical research has become increasingly important and global in recent years. We don’t have to look further than COVID-19, when health organizations, with the WHO as a supervisor, began their fight to develop the vaccine and aid in the prevention and treatment of infected patients.
Pfizer’s Phase III clinical trials enrolled 46,331 participants at 153 sites in Argentina, Brazil, Turkey, South Africa, and the United States. It goes without saying, that this increased the need for high-quality life science translation services that facilitate communication and collaboration across nations.
In this article, we will go through all the requirements of clinical research translation to live up to the standards of the global and national regulatory bodies and guarantee the advancement of science and the protection of human health.
What Is Clinical Research?
Clinical research is a subset of medical and health services research that aims to generate knowledge that can be used to better understand human disease, prevent and diagnose illnesses, and promote public health. They are supervised by academic health centers, private research institutes, survey research organizations, federal government research programs, and contract research organizations.
Clinical research is conducted to determine whether new treatments, medications, and diagnostic techniques are safe and effective for patients through rigorously controlled clinical trials. As such, it is far past basic research.
Most of these studies take time to develop, materialize, write up, peer review, and publish. They’re filled with abbreviations, symbols, and concepts that require years of education, experience, and research.
According to a Precedence Research Report, the clinical trials market was valued at approximately 48.4 billion USD in 2020. From 2020 to 2030, the market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% and reach a worth of around 84.43 billion USD.
North America is still the fastest-growing region with the largest revenue, followed by Europe and the Asia Pacific. Based on the report, Phase III dominated the global clinical trials market in 2020 with the highest market share. Phase III includes cross-national trials that recruit non-native participants, increasing the demand for clinical document documents.

5 Main Groups of Clinical Research
According to FDA, clinical research includes:
- Treatment Research – studies new devices, approaches, medication, physiotherapy, and their effect on human health.
- Preventive Research – studies medicines, nutrients, vaccines, and lifestyle changes.
- Diagnostic Research – studies new ways to identify a disorder, condition, and illness.
- Genetic Research – studies how genes impact health, and the relationship between certain genes and illness which can be researched in animal models as well.
- Epidemiological Studies – studies diseases in groups of people to find the causes, frequencies, patterns, and distribution.
Typical Documents that Need Clinical Research Translation Services
- Patient Consent Agreements
- Patient Recruitment Materials
- Patient Source, Admission, and Discharge Documents
- Patient Questionnaires and Surveys
- Clinical Trial Protocols and Reports
- Toxicology Reports
- Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs)
- Pharmacological Studies
- Datasheets
- Master Batch Records (MBRs)
- Product Labels
- Package Inserts and Labels
- Dossiers
- Development Safety Update Reports (DSURs)
- Instructions for Use (IFUs)
- Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse Reactions (SUSARs)
- Study Protocols
- Scientific Papers
- Regulatory Documents
- QoL Scales
- Websites, Apps, and Platforms
Why Is Clinical Research Translation Important: The Coronavirus Case
Clinical research is possibly the most important field of research in the world because it involves disseminating knowledge and expertise to maintain and improve the health of patients; prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases; and increase our quality of life. It is about sharing and contributing to medical innovations and addressing health issues from all over the world.
A large part of scientific research is not only coming up with questions and precise methods to answer them, but also collaborating between different organizations, researchers, patients, and individuals who do not speak the same language.
The findings of one particular study can help other scientific questions take shape and advance. By sharing all of this knowledge across languages, we can continue to innovate and help transfer knowledge and discovery to a new location. When research reaches more people, academics, businesses, volunteers, and donors, it can also help increase investment in fundamental research.
Coronavirus is an excellent example of how difficult it is to conduct clinical research. What began in one country has spread throughout the world, increasing the need for local research as well as global coordination and collaboration.
The research points out that an overwhelming number of COVID-19 clinical trials lacked methodological rigor and adequate planning. According to the scholars: Investing in large-scale clinical trials that can facilitate international collaboration will be important to generate high-quality data efficiently that can inform policy and change clinical and public health practices.
Their observation is supported by Slator and Market Research Future which state that clinical trial translation spending increased by 20% in 2020 only and the translation service market grew by 40% in the same year. CSA Research also reported that the pandemic triggered an increase in demand for translation services in healthcare (by 49%) and life sciences, medical, and pharmaceutical sector (by 38%).
What Are Some Requirements for Clinical Research Translation?
As one of the most regulated industries in the world, the translation of all medical documents, particularly research documents, necessitates exceptional service. We provide three main requirements that must be fulfilled by your LSP of choice:
1. Precision
All medical translations should meet the requirements and standards set by international and national regulatory authorities and more so if they’re clinical research that involves real consequences on patients™ health. Professional medical translators deal with more than just precise word-for-word translation. They have to be fluent in medical terminology and have advanced knowledge of protocols, and medical translation types.As a highly technical field, medical translators can be specialized in different directions such as genetics, pharmacology, epidemiology, oncology, etc.
They should also be up to date with the existing body of research and recent innovation in the field. As such clinical research translators can be classified as researchers in themselves since they have to deal with translational science which is the field of research aimed to understand the fundamental principles of science.
2. Compliance with Regulatory and Standard-Setting Authorities and Laws
In contrast to other studies, clinical research takes longer and follows a slower procedure to ensure no errors are made. As a result, a long chain of quality assurance and quality control processes is in place, with each country having a complex regulatory system that is also standardized by international bodies.To give you an idea, a principle of Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines is that the well-being of the participant is more important than that of the study or society at large.As a result, even before the clinical trial begins, all risks should be meticulously measured, and the investigators should ensure that no harm will be inflicted on the participant.
A clinical trial can begin only after regulatory bodies have reviewed and approved this statement’s accuracy.Another important element is record-keeping; Every step taken during the clinical trial is accompanied by a document that should be compiled and stored in a way that ensures accurate reporting, and allows for verification.In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for ensuring the safety and efficacy of drugs, biological, and device products in the United States. That includes regulating all research on new drugs or devices that intervene in human health to prevent, diagnose or treat different medical conditions. In the European Union, the equivalent institution is the European Medicines Agency (EMA). Other examples of organizations that set standards in clinical trials include:
- Japan’s Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA)
- Canada’s Health Canada
- Switzerland’s Swissmedic
Some global bodies that regulate clinical research include:
- International Compilation of Human Research Standards: This institution consists of over 1,000 standards on human subjects’ protection in 131 countries such as laws, regulations, and guidelines.
- CAMPUS for Regulatory and Ethical Requirements: Ensures that sensitive information and confidential data are protected and secure.
3. Cultural Sensitivity
Personal experience and culture influence how the research community thinks about their questions, methods, and population. As a result, when translated to a new culture, the same procedures, questionnaires, and wording must be adapted to stay relevant to the new target population.In consent forms, patient information forms, and the like, patients should be able to clearly understand each word and sentence and not find it invasive, confusing, or, worse, offensive.Furthermore, cultural patterns must be incorporated into research design, conduct, and interpretation as well.
By properly including different target groups and being aware of how they function, we ensure diversity which helps improve the outcomes of the study findings and their veracity.We must exercise extreme caution when copying and pasting the same clinical research document from, say, a Western perspective to a non-Western country. As a result, cross-cultural clinical research presents numerous challenges that necessitate cultural sensitivity on the part of the translation service providers as well.
The Stages Of Clinical Research Translation
As one of the most regulated industries in the world, the translation of all medical documents, particularly research documents, necessitates exceptional service. We provide three main requirements that must be fulfilled by your LSP of choice:
1. Precision
All medical translations should meet the requirements and standards set by international and national regulatory authorities and more so if they’re clinical research that involves real consequences on patients™ health. Professional medical translators deal with more than just precise word-for-word translation. They have to be fluent in medical terminology and have advanced knowledge of protocols, and medical translation types.As a highly technical field, medical translators can be specialized in different directions such as genetics, pharmacology, epidemiology, oncology, etc.
They should also be up to date with the existing body of research and recent innovation in the field. As such clinical research translators can be classified as researchers in themselves since they have to deal with translational science which is the field of research aimed to understand the fundamental principles of science.
2. Compliance with Regulatory and Standard-Setting Authorities and Laws
In contrast to other studies, clinical research takes longer and follows a slower procedure to ensure no errors are made. As a result, a long chain of quality assurance and quality control processes is in place, with each country having a complex regulatory system that is also standardized by international bodies.To give you an idea, a principle of Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines is that the well-being of the participant is more important than that of the study or society at large.As a result, even before the clinical trial begins, all risks should be meticulously measured, and the investigators should ensure that no harm will be inflicted on the participant. A clinical trial can begin only after regulatory bodies have reviewed and approved this statement’s accuracy.
Another important element is record-keeping; Every step taken during the clinical trial is accompanied by a document that should be compiled and stored in a way that ensures accurate reporting, and allows for verification.In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for ensuring the safety and efficacy of drugs, biological, and device products in the United States. That includes regulating all research on new drugs or devices that intervene in human health to prevent, diagnose or treat different medical conditions. In the European Union, the equivalent institution is the European Medicines Agency (EMA). Other examples of organizations that set standards in clinical trials include:
- Japan’s Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA)
- Canada’s Health Canada
- Switzerland’s Swissmedic
Some global bodies that regulate clinical research include:
- International Compilation of Human Research Standards: This institution consists of over 1,000 standards on human subjects’ protection in 131 countries such as laws, regulations, and guidelines.
- CAMPUS for Regulatory and Ethical Requirements: Ensures that sensitive information and confidential data are protected and secure.
3. Cultural Sensitivity
Personal experience and culture influence how the research community thinks about their questions, methods, and population. As a result, when translated to a new culture, the same procedures, questionnaires, and wording must be adapted to stay relevant to the new target population.In consent forms, patient information forms, and the like, patients should be able to clearly understand each word and sentence and not find it invasive, confusing, or, worse, offensive.Furthermore, cultural patterns must be incorporated into research design, conduct, and interpretation as well. By properly including different target groups and being aware of how they function, we ensure diversity which helps improve the outcomes of the study findings and their veracity.
We must exercise extreme caution when copying and pasting the same clinical research document from, say, a Western perspective to a non-Western country. As a result, cross-cultural clinical research presents numerous challenges that necessitate cultural sensitivity on the part of the translation service providers as well.
The Stages Of Clinical Research Translation
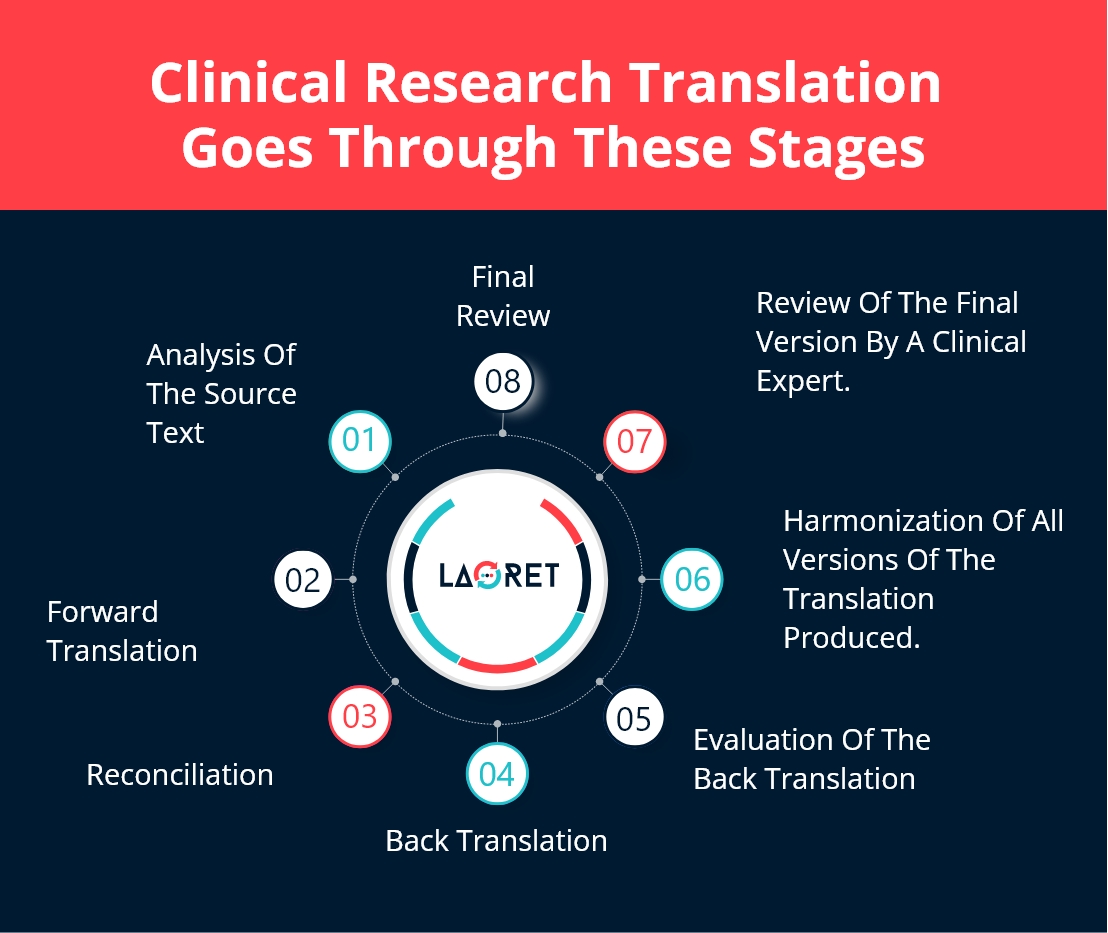
An elaborate translation process carried out by efficient and professional LSPs is as follows:
- Analysis of the source text before the actual translation process, to make sure everything is error-free and ready to be translated.
- Forward translation of the source text into the target language in more than one version by at least two translators who work independently.
- Reconciliation of the versions of the translated text from a Subject-matter Expert (SME) that produces the best version.
- Back translation of the text from the target into the source language.
- Evaluation of the back-translated versions of the document with the original. Here, issues are resolved and a final translation is generated.
- Harmonization of the back translation in multiple languages.
- Review of cognitive debriefing results by a clinical research expert in the specific subject matter.
- Final review and report by the translation, editing, and proofreading team based on feedback from the clinical research expert.
Download our comprehensive checklist
Get your free guide to help you plan your next virtual interpreting event!
How to Pick an Expert Medical Translation Service Provider?
To summarize, you should bear at least these three considerations in mind before selecting the LSP who will assist you with your clinical research translation project:
- Native Subject-matter Experts: The team selected to work on the translation, editing, and proofreading should have extensive knowledge of the medical field in which the research is being conducted. They must be able to deal with the topic’s complexities while also paying attention to the terminology and nuances of the field.
- Use of CAT tools and Machine Translation: Although human supervision and editing can help refine and sharpen the final results, automation allows for faster turnaround times. Advanced automated tools are excellent for facilitating work with medical glossaries and terminology while also keeping the text consistent and understandable for the target audiences.
- Quality Assurance: Back translation, machine translation post-editing MTPE, and CAT tools all help to ensure that the medical document’s translation is accurate. However, quality assurance includes more elements and follows a complex process to avoid miscommunication and confusion. Two main ISO certifications that LSPs should have are:
- ISO 9001: focuses on meeting customer needs, delivering what was promised to customers, and improving the overall quality of products and services.
ISO 17100:provides requirements for the core processes, resources, and other aspects necessary for the delivery of a quality translation service.
Conclusion
Whether you need clinical trials, case reports, patient information leaflets, or any other documentation translated, our network of subject matter experts offers clinical research translation services in over 120 languages. Request a quote here or contact us to tell us more about your project. Let’s discuss your case and requirements without any commitment from your side.
References
- Statista: The world’s most spoken languages
- World Data: The world’s largest economies
- Internet world users by language
- The 10 Largest E-Commerce Markets in the World by Country
- English levels in China
- The most used languages on the internet
- China: Language simplification to increase literacy?
- The main differences between Mandarin and Cantonese
- The Spanish language in the world
- Internet world users by language
- The U.S. Has the Second-Largest Population of Spanish Speakers” How To Equip Your Brand To Serve Them
- Parker pens make you pregnant, and other due diligence fails!
- Arabic Speaking Countries
- Arab economies to post 5.4 percent growth rate this year on higher oil prices
- More Arab countries are seeking to orient their economies towards knowledge
- Individuals using the Internet (% of population) – Arab World
- French speaking countries
- English Loses Currency as Europe’s Lingua Franca After Brexit Vote
- The rise of Africa’s digital economy
- Mechanical Engineering Industry in Germany: Our Industry Report
- Internet user penetration in Germany from 2018 to 2027






