Life Science Translation Services: Key Requirements & Trends
From pharmaceutical companies to medical research organizations, the need for accurate and reliable translation services in the life science industry has never been greater. More and more companies are preparing to launch their products and services in new locations.
In this costly industry, translation services are but a small fraction of the budget that can yield exceptional results in ROI. Nonetheless, if you make the wrong choice of partners, the risks are high.
In this blog post, we will delve into the importance of life science translations and why they are crucial for the growth and advancement of the medical industry. We will also explore the various types of life science translation services available and how to tackle the challenges that come with expanding to new markets.
What Does Life Science Industry Include?
The life science industry includes businesses and organizations that study human health and diseases and develop interventions to preserve and optimize human well-being. Its various branches include pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, environmental sciences, biomedicine, nutraceuticals, neuroscience, cell biology, biophysics, and many others.
What Does Life Science Include:
- Pharmaceutical – Develops drugs and medications used to prevent illness and medical conditions. (Products: aspirin, antibiotics, vaccines)
- Biotechnology – Combines technology with biology to improve human health. (Medical devices: blood pressure monitors, syringes, wheelchairs)
- Biomedicine – uses biological processes, organisms, or systems related to human health. (Products: GMO crops, biofuels, therapeutic proteins)
- Nutraceuticals – Develops food-based products with medical benefits. (Products: vitamins, minerals, herbal supplements)
- Neuroscience – Studies the structure and function of the brain and nervous system. (Products: brain-computer interfaces, neuroprosthetics, psychiatric drugs)
Translating life science documents is a highly regulated field with strict quality control measures in place. As such, linguistic validation, certifications, and expert knowledge are necessary to maintain ethical standards and protect both human health and scientific integrity.
In addition, any attempt to test, promote, and sell drugs and medical devices across borders requires constant cooperation between multilingual experts.
For instance, pharmaceutical companies that want to manufacture any drug or supplement abroad should translate numerous health and safety materials, standard operating procedures, and more.
From seeking approval to run the operation to clinical trials, and marketing campaigns, life science companies require a technical translation that goes beyond just medical translation services and often engages subject matter experts only.
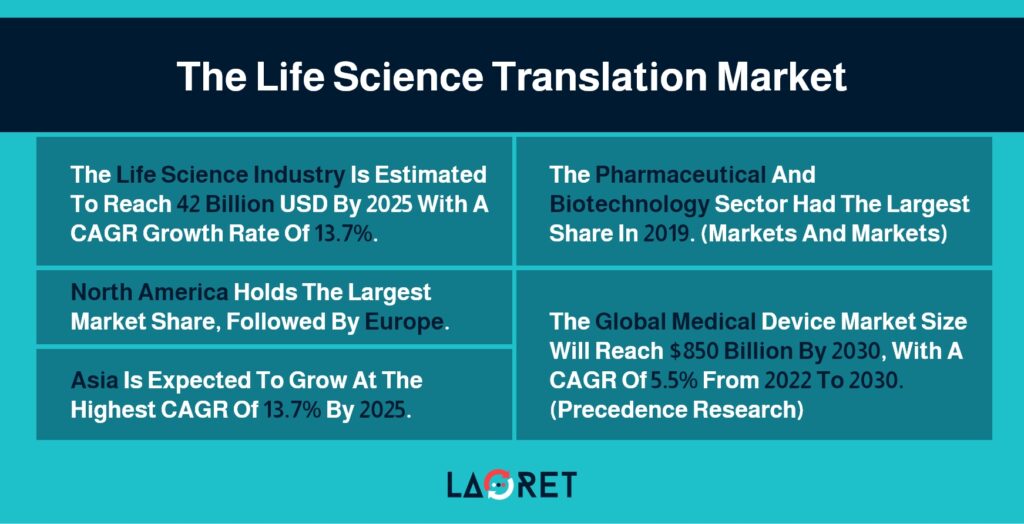
According to a report by Markets and Markets, the life science industry is estimated to reach 42 billion USD by 2025 with a CAGR growth rate of 13.7%. On the basis of region, North America holds the number one spot, followed by Europe. However, Asia is expected to grow at the highest CAGR of 13.7% for the forecasted time.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sector had the largest share in 2019. Both these subsectors aim to design, and test products such as drugs, medical devices, and treatments, that can be of use within the healthcare system.
According to Precedence Research, the end users that utilize these products the most are hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers, followed by clinics.
To bring these products to these end users, life science companies are obliged to conduct clinical trials which are a multi-stage process that evaluates the safety and efficacy of the product. There are four phases involved in the clinical trial process, and each stage must be completed with thoroughness and accuracy.
The last phrase includes testing medical devices in transnational audiences. In order for that to happen, all the documentation has to be translated and adapted to the participants. This includes user manuals, patient consent forms, questionnaires, and other critical information.
Life science documents that require translation
- Marketing materials
- Instruction manuals
- Clinical Trial recruitment and retention
- import/export permits
- Packaging and labeling
- Site documentation and reports
- Physician letters
- Investigator brochures
- Protocols and case report forms
- Patient and clinician education
- Linguistic validation
- Clinical Regulatory
- Summary of product characteristics (SPC)
- Clinical reports
- Registration documents
- Product information leaflets
- Research materials
- Protocols
- Documents
- Clinical Studies
Accurate translation of life science documents provides dual benefits. Firstly, it helps with regulation compliance and Good Clinical Practice (GCP). Secondly, it ensures that patients have a clear understanding of the trial to sign the informed consent forms.
Moving forward, clinical trials are but a part of the life science translation industry. Another example would be a novel medical device that can be used for hair implants. While the product can be patented and manufactured in Germany, the company may decide to enter the Turkish market, where there is a high demand for products in that sector.
This would necessitate investing in training Turkish personnel on the device, translating all required documents, and negotiating with relevant authorities and potential business partners.
2023 Trends and Challenges in the Life Science Translations
Life sciences are heavily influenced by new discoveries in technology, clinical research, and updated regulations. As a result, with the fast-changing nature of these factors, new challenges constantly emerge within the industry.
Speeding the Process with the Help of & AI and Machine Translation Tools
Life sciences are much slower than other fields because they require meticulous record-keeping and documentation at every step of the way. To improve this, industry leaders are investing heavily in machine translation and AI.CSA research found that one big problem in the advancement of life science is the insufficient number of human translators when compared to the demand for translation services. According to the analysis because of this issue, only 0.00000008% of the data generated daily is likely to be translated. The future for the experts is clear: the use of technology will enhance rather than undermine the work of human translators. The ideal solution is a combination of Machine Translation Post-editing services and tools, such as CAT and translation memory, that assist medical translators in dealing with the high demand and other complications that come with the job. This combination helps to leverage their expertise in both subject matter and bureaucracy, as well as cultural nuances, to deliver accurate and culturally appropriate translations.
Regulations Compliance with the Updated Laws
As technology advances, the number of pharmaceuticals and medical devices is increasing exponentially which brings the necessity to update regulations frequently. The Medical Device Regulation in the European Union, for example, was updated in May 2021 and introduced new responsibilities for the European Medicines Agency (EMA). One quality control used in the EU is the CE marking which shows the manufacturer has checked that these products meet EU safety as well as have no significant adverse events.
By having the CE marking any product is free to move within the European market. The recent revision in regulations now mandates that life science translation services must be utilized before a manufacturer can obtain CE marking. This requirement was not present before. Currently, manufacturers must translate their documentation into all 24 official languages of the European Union with accuracy and clarity. Subsequently, obtaining CE marking also falls under the manufacturer’s responsibility. These changes, even though they might seem subtle, might jeopardy your whole localization project if not taken into consideration. And each region and country has its own specifics and regulations.
Compliance with each of them demands the highest levels of expertise and professionalism, from the project managers to the medical translators. Life science translation faces many challenges which require subject matter experts who understand the bureaucratic language of laws and regulations.
Adapting to the Cultural Context
It’s easy to lose sight of the local context when dealing with global projects. While most life science documents follow strict templates with little room for interpretation, when translated into a new language, the terminology may suffer changes. Effective terminology management systems, for example, play a crucial role in helping life science translation services adapt to new cultures and maintain consistency across all documents.
In addition to complying with local regulations, certain documents should be tailored to the new audience and fit the local cultural norms. Patient questionnaires and marketing materials should be communicated in a language that resonates with the target audience. Only native subject matter experts with a deep understanding and extensive experience can effectively adapt translated documents for local audiences.
Prompt Turnaround Time
Life science translation must be 100% accurate; no mistakes are permitted. And, as previously stated, this industry necessitates extensive documentation at each stage. The more complex and risky the product, the more documentation is required. Furthermore, a delay in the process can have a domino effect on the rest of the project, so having the necessary capacity to deliver high-quality translation and being quick to solve any problems that may arise is critical. The translation services should keep up with the industry’s fast pace and be able to respond quickly to changes and updates within the project as well as external ones such as technology and medical research updates and innovations.
Requirements for a High-Quality Life Science Translation Project
-
Partnering with the Right LSP
For successful translation of life science documents, it is crucial to partner with a professional and specialized LSP with the relevant certifications. ISO 17100 certification is a must-have in handling life science translation projects because it guarantees that the LSP meets high standards for quality, efficiency, and consistency in their translations and that the proper management systems are in place. This provider must have native subject matter experts with a deep understanding of local regulations, bureaucratic language, and cultural context. This will ensure the project progresses smoothly and facilitate efficient turnaround time.
-
Implement Top-Notch Data Confidentiality Measures
Life science translation often involves handling delicate and confidential information about individuals and intellectual property. It is crucial to choose an LSP that has a secure system in place to protect this information from being lost, shared, sold, or used without authorization. To safeguard sensitive data, it is advisable to ensure that strong security measures such as encrypted files and secure data storage are in place. This will prevent unauthorized access or theft of the data.
-
Quality Assurance and Linguistic Validation
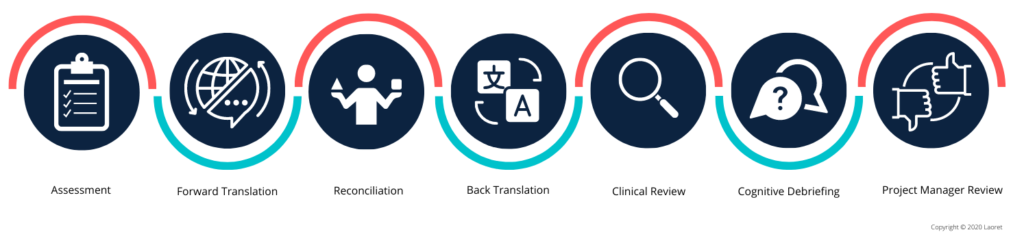
In the life sciences industry, expertise, precision, and timeliness are critical. Ensuring quality starts with delivering accurate source documentation to the LSP at the beginning of the project, which can hasten the translation process. The LSP then takes the lead in overseeing a thorough quality assurance process that includes key steps such as translation review, back translation, reconciliation, medical expert review, etc.
- Translation Technology
The integration of translation technology and AI tools in the work of human translators can significantly improve the quality of work in industries such as life sciences. With the aid of tools such as terminology management and translation memory, the accuracy of the work is greatly improved. For example, terminology management tools allow translators to maintain a centralized database of specialized terms used in life sciences. This database can be accessed by multiple translators and updated as new terminology emerges.
Download our comprehensive checklist
Get your free guide to help you plan your next virtual interpreting event!
Conclusion
In today’s globalized world, it is imperative that medical information and research are accessible to a wider audience. By breaking language barriers, industry leaders can make the process more convenient for participants, gain better research results, and lower the number of failed trials. Life science translation requires a high level of scientific and technical expertise compared to general medical translation types. Laoret supports your pursuit of launching medical devices and drugs in new markets through native subject matter experts. Request a quote today and see how our team can help you reach new heights in your research and global localization efforts.
References
- Statista: The world’s most spoken languages
- World Data: The world’s largest economies
- Internet world users by language
- The 10 Largest E-Commerce Markets in the World by Country
- English levels in China
- The most used languages on the internet
- China: Language simplification to increase literacy?
- The main differences between Mandarin and Cantonese
- The Spanish language in the world
- Internet world users by language
- The U.S. Has the Second-Largest Population of Spanish Speakers” How To Equip Your Brand To Serve Them
- Parker pens make you pregnant, and other due diligence fails!
- Arabic Speaking Countries
- Arab economies to post 5.4 percent growth rate this year on higher oil prices
- More Arab countries are seeking to orient their economies towards knowledge
- Individuals using the Internet (% of population) – Arab World
- French speaking countries
- English Loses Currency as Europe’s Lingua Franca After Brexit Vote
- The rise of Africa’s digital economy
- Mechanical Engineering Industry in Germany: Our Industry Report
- Internet user penetration in Germany from 2018 to 2027






