The Ultimate Guide to Translation Quality Assurance
Mistranslation of a campaign in several locations forced HSBC, the largest bank in the UK (2021), to spend 10 million USD in rebranding during a highly volatile economic situation in 20091. The mistake was as naive as translating Assume nothing into Do nothing which gave the wrong message to the target audience.
Today, this case serves as a cautionary tale to any business trying to expand to foreign markets. A proper translation quality assurance (TQA) is the guarantee that the translation and localization company (TLC) of your choice will meet your needs and requirements as well as avoid any embarrassing or costly mistakes.
In this article, we go through all the elements of high-quality assurance in translation to help you choose and work with the right language partner.
Why Do You Need Translation Quality Assurance?
It’s all about the quality of your multilingual quality. But how can translation quality assurance achieve for your business?
-
Reach Your Business Goals and Target Audience
The first thing that probably pops into your head when you hear the word translation quality assurance is accuracy. And that’s true, the content should be linguistically and grammatically accurate. However, beyond accurate translation, the content purpose should stay intact, and that requires maintaining the appropriate language tone.
Furthermore, each brand has its own style guide or a set of standards for both written and visual materials that the translation service provider should follow meticulously. So, not only linguistic quality of the translated text should reflect your business goals, be it brand awareness or increased conversions, and speak to the target audience‘s pain points, but the tone and visuals as well.
With a high-quality language service provider, the TQA starts and ends with a very efficient project manager who can build bridges between the quality requirements and business needs of the clients and the expertise of the team.
-
Present Your Brand Correctly in the New Market
Global expansion can be tricky because every product or service is created and built in a certain social context which might not fit in different parts of the world. Consider all the foreign brands or marketing campaigns that sounded absurd in your native tongue. Or brands that ignored the sensitivity of a topic in a given society and received a massive backlash. Surely, these campaigns did attract attention, but in the long run, they didn’t build sustainable brands.
With strict TQA, translation service providers should be able to translate the product or service accurately, taking into account the cultural nuances of your target markets. This is while conveying the precise tone and mission of your brand.
Does Translation Quality Assurance Equal High-Quality Translation?
Translation quality is one of the objectives of translation quality assurance required to translate and localize your brand successfully, but what does quality mean in translation?
What Does Quality in Translation Mean?
Simply put, a high-quality translation adheres to the standards set by the recognized authorities of the local language including grammatical and syntactical rules, sentence structure, etc. Beyond proper spelling and the like, an example of quality in translation would be writing in the proper date format, which differs from country to country. The USA has a unique date format that starts with the month (mm/dd/yyyy). Using the same format in the Middle East would leave many people confused since they use another date format (dd/mm/yyyy).That would cause a problem because if that date announces the end of a sale or an inauguration event, a large profit will be “lost in translation, and surely so does quality. Your in-house marketing team may be unaware of such differences; however, if you collaborate with a local team of translators, you would avoid many similar mistakes. Learn more about how to receive top-quality translations that are also cost-effective!
What’s Translation Quality Assurance?
Translation Quality Assurance is a set of procedures, or a multiple-layered filter, that ensures your translated content is linguistically and technically accurate, and consequently, your business stays on track and expands smoothly in the new market. The TQA runs before, during, and after the translation work to guarantee your product or service will be well received by the local target audience. The project management team takes measures to assure quality in translation prior to delegating work to translators, designers, and engineers and continues well after they’ve done their job. Read along to understand all the stages and elements of high-quality translation assurance.
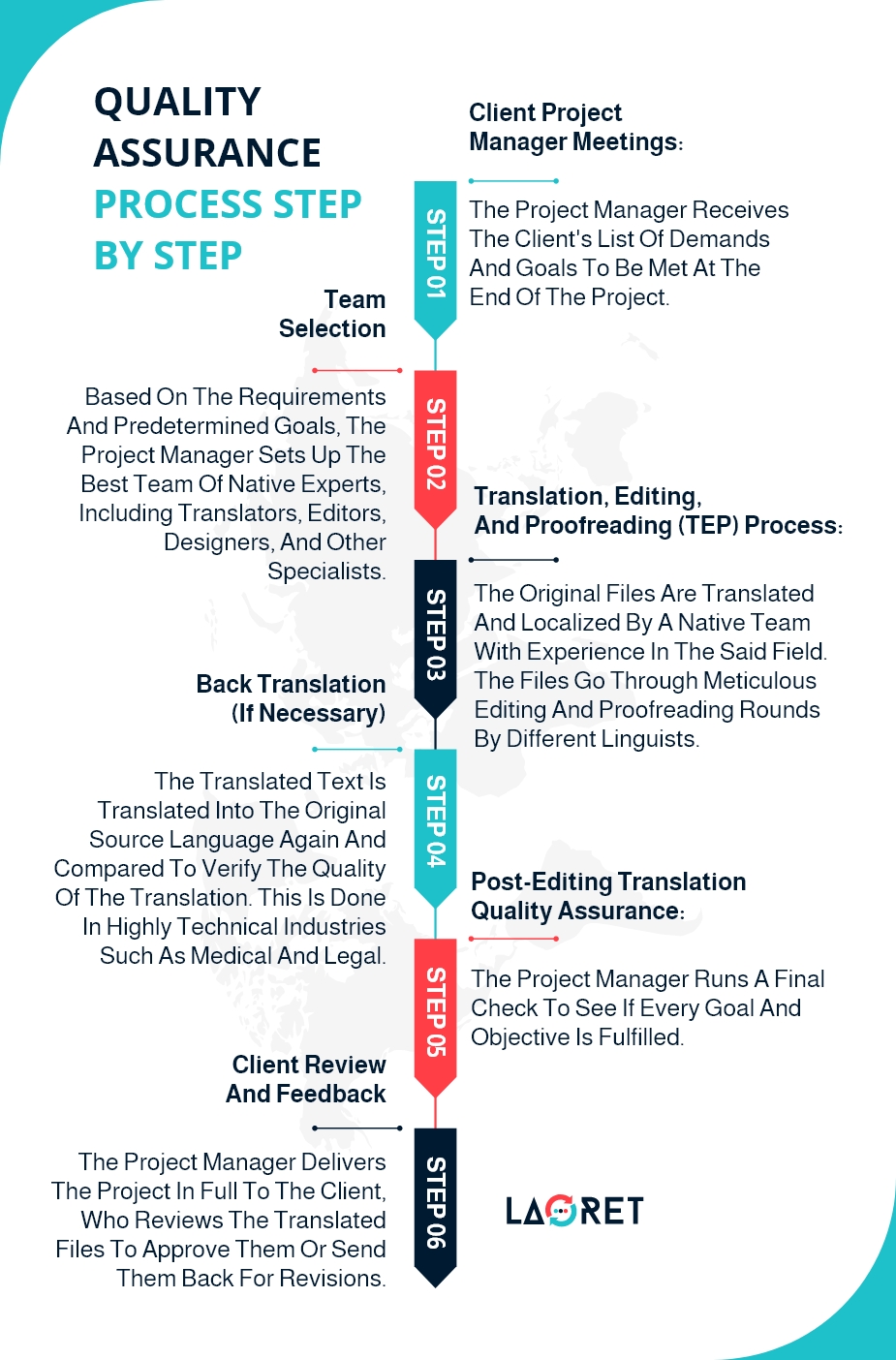
3 Stages of a High-Quality Translation Assurance
An efficient TAQ includes three stages:
1. Pre-translation Stage
Firstly, the project manager ensures that the translation and localization company receives all necessary information from the client’s side, from their big-picture expectations up to their preferences for the type of currency to be used. The source material provided by the client is also checked to see if all the files are error-free and that the translators will not encounter any difficulties during translation. The next step is team selection where the project is assigned to translators who are native speakers of the local language and have the necessary qualifications and experience in the said industry. The translation work is all integrated into a translation management system (TMS) that leverages advanced tools to manage the workflow and maintain consistency in translation.
2. Translation, Editing, and Proofreading Stage
The TMS platform centralizes all of the workflows in one location, allowing translators, editors, proofreaders, engineers, web developers, and even clients to log in and carry out tasks following the user rights assigned by the project manager. This way each task is completed and peer-reviewed within the same system. A good translation quality assurance includes a strict Translation, Editing, and Proofreading (TEP) Process and Computer Assisted Translation (CAT) throughout the translation work. Besides software and automated tools, this stage involves 3 expert linguists: translators, editors, and proofreaders, all vetted to be the best fit for the project. For example, the assigned translators must have a thorough understanding of the quality standards in a particular area of translation, such as the medical, financial, or legal field. They carry out their tasks and then send the files over to be edited and proofread. After all the files are translated, editors perform a second round of proofreading to check for structural, content, and grammatical errors in the target language and make sure that it reads naturally. One of the aforementioned CAT tools used is the Translation Memory (TM) which saves all previously translated words and segments. By using the same translated term and phrases consistently, you save time and improve translation quality. This means you’ll never have to pay for the same translation twice, reducing costs and increasing your ROI on language translation services.
3. Post-Translation Stage
Even though the entire translation work is controlled every step of the way by different pairs of eyes, the best insurance is having yet another final layer of TQA. In the last stage of the Translation Project Management process, the post-translation stage is run by the project manager. Here, both linguistic quality, as well as the visual and functional quality of the project are meticulously examined to guarantee every goal is met. After that, the project manager sends the source and translated files to the client for feedback and approval. Any and every concern of the client or request for revisions will be communicated from the project manager to the working team and the proper changes will be made.
Here’s How to Guarantee a Language Services Provider Offers Great Translation Quality Assurance
There are many ways to make sure the translation and localization company has what it takes to offer the best Translation Quality Assurance for you. We offer a checklist to help you make the best choice for your business:
-
Having ISO Certification In Place
A translation company offering a certified translation service operates in accordance with ISO (International Organization for Standardization) certifications, which builds credibility and trust among stakeholders. That’s because ISO has been the most recognized and reputable standard-setting body since 1947. With 167 members worldwide, ISO creates and publishes international standards in both technical and non-technical fields.


Concerning translation quality assurance, the ISO 17100 is a highly sought-after certificate from both translation service-providing companies and their clients. It specifies the core processes and resources required to meet applicable specifications set by the client and the industry standard.
Another standard for general organizational Quality Management Systems (QMS) is ISO 9001. This is one of the most widely used ISO standards for developing, implementing, and maintaining a Quality Management System (QMS) for any business, regardless of industry or size.
Overall, ISO standards improve the quality of localization and translation services, help manage transnational projects more efficiently and gain access to new markets by making products and services compatible across countries.
-
Having Qualified Native Translators, Experts in the Specific Industry
A major factor in increasing the overall translation quality is the ability of the project manager to delegate the translation work to native linguists. Hiring native speakers of the local language will guarantee that the translated text reads naturally, the content is free of errors, and there are no cultural misunderstandings. However, not every native speaker is qualified to translate any technical language. As a result, you must ensure that the translation and localization team is a certified team that will deliver to the desired standard.
-
Using Both Human and Machine Translation for High-Quality Assurance
Each translation project should have a translation management system (TMS) that coordinates the workflow and integrates advanced tools and machine translation. Tools aid in the translation process by speeding it up and automating parts that do not require human expertise. Let’s take the example of the translation and localization of an eCommerce store selling kitchen appliances. While translators need to translate the product descriptions, the translation of product specifications such as dimensions can be done by machine translation which is the process of using computer software to translate. The post-editing process, however, requires the involvement of humans, where the translation done by AI is proofread and checked by a human editor for fluency and relevance.
-
Back-Translation for Highly Technical Industries
Another way to increase translation quality assurance is by performing a process called back translation. During this process, in highly technical industries where precision is paramount such as medical and legal, all the files are translated back to the source language and then compared to see if they mirror each other.
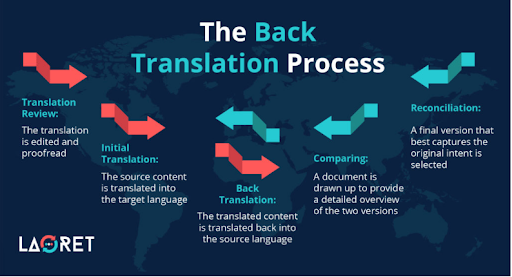
- This added level of translation quality assurance is done to make sure the translated text complies with all the regulations and standards of the field. If you operate in a highly technical industry having the option of a back translation will add to the translation quality assurance and guarantee technical precision.
Conclusion
When it comes to translating your product or service to new markets you have to make sure you’re cooperating with the right experts. While an ISO certification is a great first step in weeding out low-quality translation and localization companies (TLC), it is, by no means, a sufficient quality guarantee. You can learn more about how Laoret can help in improving translation quality assurance by requesting a quick quote.






