Clinical Trial Translation: Achieving Success in the Medical Industry
Clinical trials are now developed and conducted in various parts of the world as technology advances and internationalism grows. They can be designed, compiled, and developed in one country while the participants and data are collected in another.
This article explains in detail what goes into high-quality clinical trial translation, including documentation, regulatory bodies, ethical concerns, and other requirements.
What Are Multilingual Clinical Trials and What Documents Need Translation?
According to World Health Organization, clinical trials are a type of scientific research that investigates the effect of new drugs, medical devices, interventions such as surgery, radiology, as well as behaviors and lifestyles on human health.
As a result, the team of researchers as well as reviewers are subjected to rigorous protocols that must be approved even before the trial begins.
Clinical trials are commonly divided into observational and interventional. The first one observes the effect of different lifestyles or behaviors through testing. Meanwhile, the latter intervenes in human health through the intake of new drugs, medical devices, or surgery.
The 4 Phases of Clinical Trial
- Testing Brand-new Medications on a small sample size of patients to determine the safe dosage rate and detect side effects.
- Testing the Phase One Intervention that was deemed safe on a large scale.
- Testing on Wider Populations which may encompass entire countries and regions to make sure the intervention should be approved or not.
- If the intervention is approved in a country, it still needs to be tested in a wider population over a longer timeframe.
As the stages indicate, clinical trials will invariably involve multicultural groups speaking different languages. Proper documentation and translation of each step are required, which includes total consent and full understanding of the participants.All statistics show that there are still language barriers that must be overcome in the clinical trial industry. Even within the United States, which has the largest market share, the majority of clinical trial documents are not being translated at the appropriate rate for people with limited English proficiency.A study examining the inclusivity of clinical trials in the United States found that a significant percentage of clinical trials exclude individuals who do not speak, read, or write English at a high proficiency. For example, while more than 21.5% of Americans speak a language other than English at home, only 2.7% of clinical trials are translated into languages other than English.Inadequate translation of clinical trial documents can result in a slew of problems and errors. It may also contribute to the most pressing issue in the field today: recruiting and retaining participants. Clinical Trial Translation Fact Sheet1. As of 31 January 2023, 53% of registered studies on ClinicalTrials.gov. are outside of the USA, and 31% are in the USA.
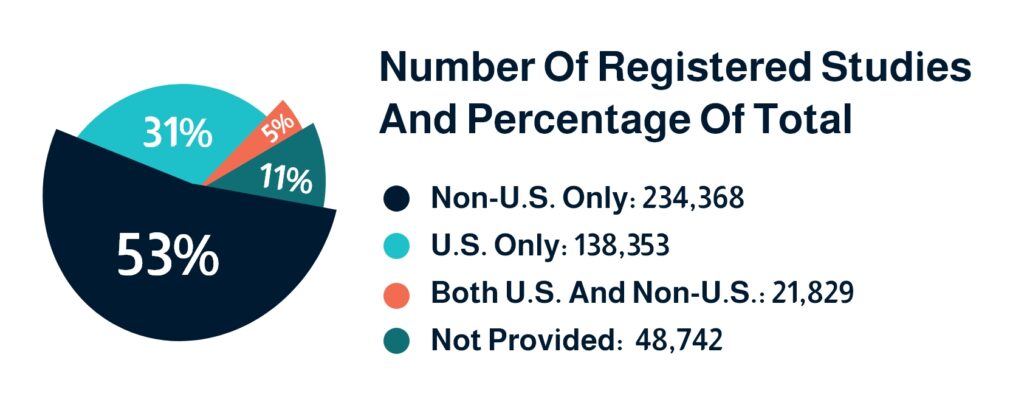
2. 95% of clinical trials are INTERVENTIONAL, with drugs and biological interventions accounting for the majority.
3. In the USA, only 2.7% of clinical trials are translated into languages other than English. (Muthukumar et al., 2021)
4. According to a report by NiceRx, these are the top ten countries conducting the highest number of clinical trials:
- United States 148,736
- France 30,080
- Canada 24,581
- China 23,509
- Germany 22,215
- United Kingdom 21,163
- Spain 16,492
- Italy 16,140
- South Korea 12,693
- Belgium 11,345
What Clinical Trial Documentation Needs Translation?
A clinical trial process is quite lengthy and procedural in the sense that there is official documentation of the process and a need for approval and awareness of many parties involved at every step of the way.
Participants are chosen at random or based on specific characteristics, for example, a trial on breast cancer treatment will only include people that suffer from it. They become part of the trial after being fully scanned and having a thorough understanding of the procedure.
Examples include testing a general health supplement on behalf of a pharmaceutical company or performing surgery to evaluate a new medical device.
As a result, participants must review numerous documents pertaining to the specific issue, as well as complete specific forms to share personal information.
One of the first documents that requires a precise and meticulous translation is the patient consent form. Participants sign a document stating that they agree to participate in full will and that they have been given enough information to make an informed decision.
Another important document is the patient questionnaire, in which they reveal vital information about their medical condition. Any misunderstanding could lead to additional complications that would not only undermine the trial outcomes but could also have undesired consequences for their health.
Other documents in need of translation include, but are not limited to:
- Adverse event reporting forms
- Patient information sheets
- Investigator brochures
- Clinical study protocol
- Investigator’s manual
- Case report forms
What’s the Importance of Clinical Trial Translation?
By providing high-quality clinical trial translation services to patients, researchers, and other stakeholders, we ensure diversity and inclusion as well as improve the medical solutions available.
Without multilingual clinical trial documents, the parties will be unable to recruit or retain patients with limited English proficiency, or the process will be delayed, potentially resulting in unwanted deviations from the agreed protocol.
If the participants and all parties involved are not fluent in the original language of the documents, there is a risk of collecting data incorrectly. On the other hand, it violates ethical standards to provide people who want to participate in the clinical trial with incomplete or inaccurate information.
Furthermore, if clinical research discoveries are inaccessible due to language barriers, the scientific community will be unable to learn from and build on each other’s work.
Lastly, the translation of clinical trials is oftentimes a requirement of the regulatory bodies. Failing to comply with language regulations may result in loss of license or other penalties. Below we’ll explain the translation requirements for clinical trials that guarantee successful realization within the set timeframe.
Current Key Requirements for Clinical Trial Translation
-
Compliance with Regulatory Bodies and Standards
To be approved for conduct, the clinical trial must meet the standards of several local and international regulatory bodies. These institutions establish standards and rules to ensure good clinical practice (GCP), which includes many elements such as meticulous documentation, translation, and reporting of all the data and processes to both protect participants and ensure confidentiality and security.These GCP guidelines are developed in the International Conference of Harmonization (ICH) based on the Declaration of Helsinki. The obligation to translate documents related to clinical trials varies from country to country. Below we list some international and regional ones:
Download our comprehensive checklist
Here’s the complete list of local and international clinical research
regulatory bodies in the world.
-
Translation Quality Assurance
Aside from the aforementioned regulations, when it comes to transnational clinical trials,translation requires a strict quality assurance process that includes linguistic accuracy and technical precision.The project starts by evaluating the clinical trial documentation and making sure they are error-free and ready to be adapted to the target language. The team of translators selected should have experience and expertise within the medical and scientific field. Translation Management Systems (TMS), CAT tools, translation memories, and other translation tools do a great job of facilitating their work and improving the precision and consistency of terminology across documents.Clinical trial translation projects involve project managers, subject matter experts, medical linguists, editors, and proofreaders that work together to continuously review and improve the final version of the documents. Part of the quality control is also exercising caution regarding confidentiality and data protection. The process must be transparent and adhere to international standards, and the results must be analyzed and evaluated by multiple teams while protecting sensitive information.
-
Cultural Relevance
When we mentioned phases, we explained how, from phases 1 to 4, the pool of people taken in a country may be made up of different minorities who speak different languages.Actually, more and more research organizations are conducting clinical trials that involve different groups, particularly minorities and people from diverse racial and environmental backgrounds. That increases the value of the study, but it necessitates adapting not only the language but also the culture. When it comes to health, there are many terms that, when translated word-for-word in a new language, can be confusing or offensive. All of these aspects should be taken into account and handled by a translation company with the proper experience and credentials in providing medical translation services.
-
Best Practices for Clinical Trial Translation
Before partnering up with a language service provider, make sure they tick all the points below:
- Hire Native Experts, including SMEs, clinical experts, proofreaders, and medical translators. Poor translation might undermine all efforts, bring health consequences for the participants, and damage the company’s credibility. Your choice of translation team should have a proven specialization in life sciences translation services.
- Involve CAT tools, Translation Memories, and terminology management. If the project contains tens of thousands of words, CAT tools enable the comparison of various versions faster than human medical translators. These tools ensure that terms are used consistently throughout a lengthy clinical study.
- Guarantee Linguist Validation. Reconciliation, back translation, cognitive debriefing, and harmonization are some of the critical steps in guaranteeing quality control in these types of translation projects.
- Understand the Different medical translation types. Documents necessary for research and stakeholders require different language filled with technical terms, meanwhile, participant documents such as information ones include a simpler and clear style so that the participants understand and engage with it.
- Adapt to cultural differences and regional regulatory authorities.
- Have a built-in integrated translation process. This ensures that the translation company handles all documentation in a comprehensive manner by utilizing a centralized translation management system.
- Protecting confidentiality is a major ethical concern that will be scrutinized by regulatory bodies, and it can cause disapproval if not followed properly.
Conclusion
Translation services for clinical trials should be provided at each stage, to ensure consistency and coherence. Laoret has a great team of native subject-matter experts who can handle any clinical trial project and deliver a technically accurate translation in over 120 languages. Apart from our expert team, we are backed up by the latest technologies that ensure linguistic validity and efficiency. Contact us to learn more.
References
- Statista: The world’s most spoken languages
- World Data: The world’s largest economies
- Internet world users by language
- The 10 Largest E-Commerce Markets in the World by Country
- English levels in China
- The most used languages on the internet
- China: Language simplification to increase literacy?
- The main differences between Mandarin and Cantonese
- The Spanish language in the world
- Internet world users by language
- The U.S. Has the Second-Largest Population of Spanish Speakers—How To Equip Your Brand To Serve Them
- Parker pens make you pregnant, and other due diligence fails!
- Arabic Speaking Countries
- Arab economies to post 5.4 percent growth rate this year on higher oil prices
- More Arab countries are seeking to orient their economies towards knowledge
- Individuals using the Internet (% of population) – Arab World
- French speaking countries
- English Loses Currency as Europe’s Lingua Franca After Brexit Vote
- The rise of Africa’s digital economy
- Mechanical Engineering Industry in Germany: Our Industry Report
- Internet user penetration in Germany from 2018 to 2027






