7 Reasons Why Mobile App Localization Matters
Localization, as a market expansion strategy, can help mobile apps gain traction in new markets and increase revenue.
But you can’t expect users from different regions to want to use your app if it’s featured in a language they don’t understand. Navigating these regions with their multitude of languages and cultures is essential for global success. So, if you want to enter the charts, mobile app localization is your best bet.
7 Reasons to Localize Your Mobile App
Mobile app localization can mean a lot of things, from translating the whole content and adding local currencies and date formats to something as straightforward as translating your app store listings.
50% of mobile app users base their decision solely on the first impression. So you only have a few seconds to persuade users. What better way to do so than by speaking in their native language?
Below, we list all the reasons, backed by data, for how a solid mobile app localization strategy is your ultimate app growth strategy.
1. Increase Market Share and Revenue
Mobile app localization is an essential step for mobile app developers looking to expand their market share globally.
But it’s a make-or-break necessity. In fact, statistics show that apps that don’t implement localization can lose up to 13% of their users.One example is Clash of Clans, which gained a significant market share after localizing the app in multiple languages. After releasing the “Gold Pass” update in 2019, user spending doubled in less than a week. Currently, most of the non-US Clash of Clans users are from Turkey, China, Germany, and Russia, where users prefer content in their native language.
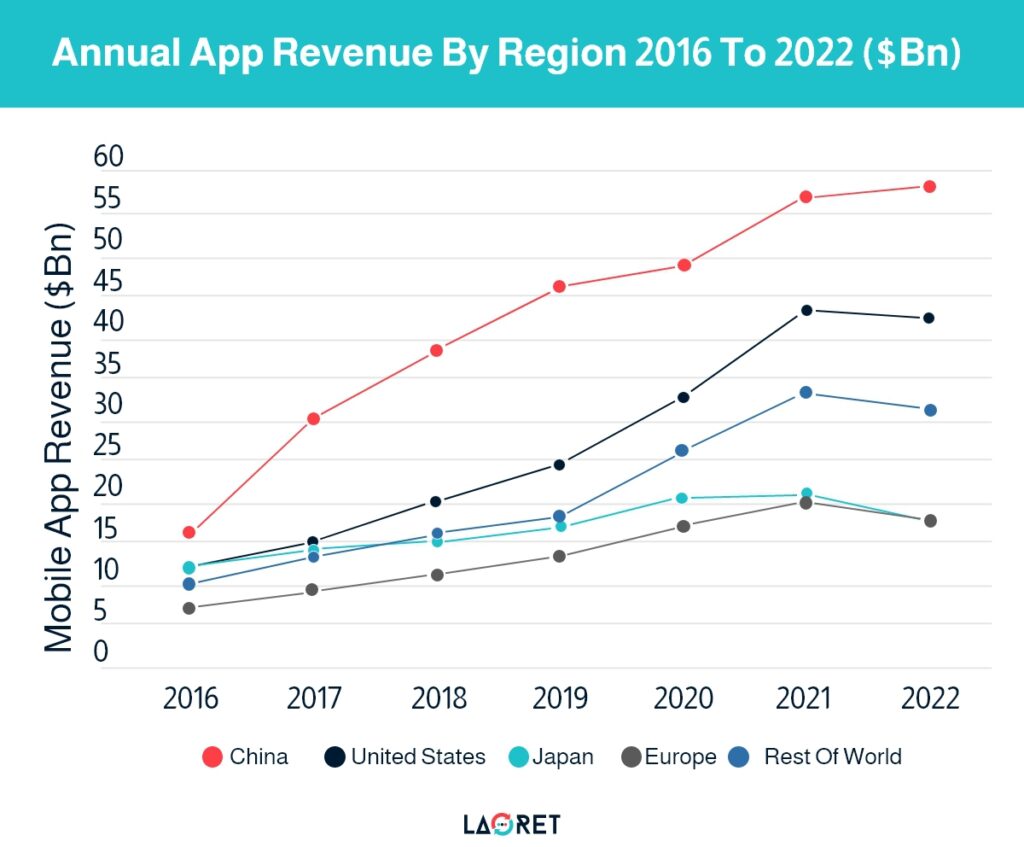
Even though your product might be great and loved in its local market, you might be putting constraints on your entire business growth. When you localize your mobile app for particular markets with growth potential, you are opening up for greater market share and revenue possibilities.
Many app developers get discouraged by the mobile app localization cost, but the return on investment can far outweigh the initial cost. Even if you only focus on localizing the keywords in the iOS App Store, for instance, you can expect a staggering 767% increase in downloads. You do the math.
But success is, of course, dependent on the quality of the application localization process.
A well-executed app localization process requires professional translation and careful attention to cultural nuances and linguistic differences to ensure a seamless user experience.
2. Improve User Experience and Engagement
Only 0.5% of apps succeed, and the primary reason for this is a lack of user engagement. If users aren’t invested in your app, your product is rendered ineffective. To attract users, it’s important to grab their attention within the first few seconds and provide them with a functional and user-friendly mobile app that meets their needs. In fact, 62% of users will uninstall an app if it crashes or freezes frequently.This brings us to a common misconception: localization goes beyond translating your app text into another language. With customer-centricity at its core, mobile app localization is a cross-disciplinary approach that takes into account your app’s content, user interface, and app performance.
On the bright side, localizing mobile apps for different languages and cultures can lead to 128% more downloads per country, and increase revenue by 26% for each country added.

However, this requires conducting thorough market research to understand the preferences and expectations of the target market. For example, you need to consider the popular categories of mobile apps in your target market and which mobile app stores are most frequently used.
Additionally, to successfully localize a mobile app for both iOS and Android, it’s important to follow platform-specific design guidelines. For instance, Android app localization requires attention to the fragmentation of the Android ecosystem, including different screen sizes and operating system versions.
3. Gain a Competitive Advantage Over Other Apps
By the end of 2022, over 3.55 million apps were available on the Google Play Store and another 1.6 million on the iOS App Store. With so much competition, the goal is to create a product that stands out from the rest. Design Consider this example: Let’s say you developed a medical mobile app that is missing in a particular target market. Even if your product is superior to any other similar one, the target audience won’t download it if it’s not available in their native language. However, by opting for a medical mobile app localization process, you can let the superiority of your product speak for itself. Localized apps have a clear competitive advantage over non-localized apps. When a user searches for an app, there are just too many to choose from that offer the same thing. But if they come across an app that’s featured in their local language and that’s personalized to their needs and interests, they’ll stop scrolling and choose it over its non-localized counterparts.
4. Boost Brand Visibility and Credibility
When you introduce yourself to someone, you naturally use language and words that they understand to ensure they can empathize with you. This becomes even more significant when selling your product to potential customers. The most common mistake app developers make is considering localization only as a revenue-generating strategy, which it is. However, the impact of a localized app goes beyond numbers.
If done right, mobile app localization is an opportunity to enhance your visibility and establish credibility. But, what if one of those target markets becomes your primary source of revenue? And you completely missed it due to sloppy localization?Take the example of two mobile apps that are crashing local competitors. The first one is Duolingo. It withdrew from China to come back stronger at the end of 2022 with a local twist, tailoring its services and offering lessons in Cantonese, the local language of Hong Kong.Secondly, the Uber app is localized in over 30 languages and has a variety of local features, including in-app language translation, establishing an international name for global audiences and driving its success in diverse markets.
5. Reach New Markets and Global Audiences
Data from App Annieshows that half of the countries in the top 10 list for iOS app downloads and revenue are non-English speaking countries from East Asia and Europe.
Accordingly, to maximize revenue in iOS App Store, app developers need to consider the global market beyond the US. East Asian countries with non-Latin writing systems occupy the number two spot behind the US in terms of free downloads and revenue share.
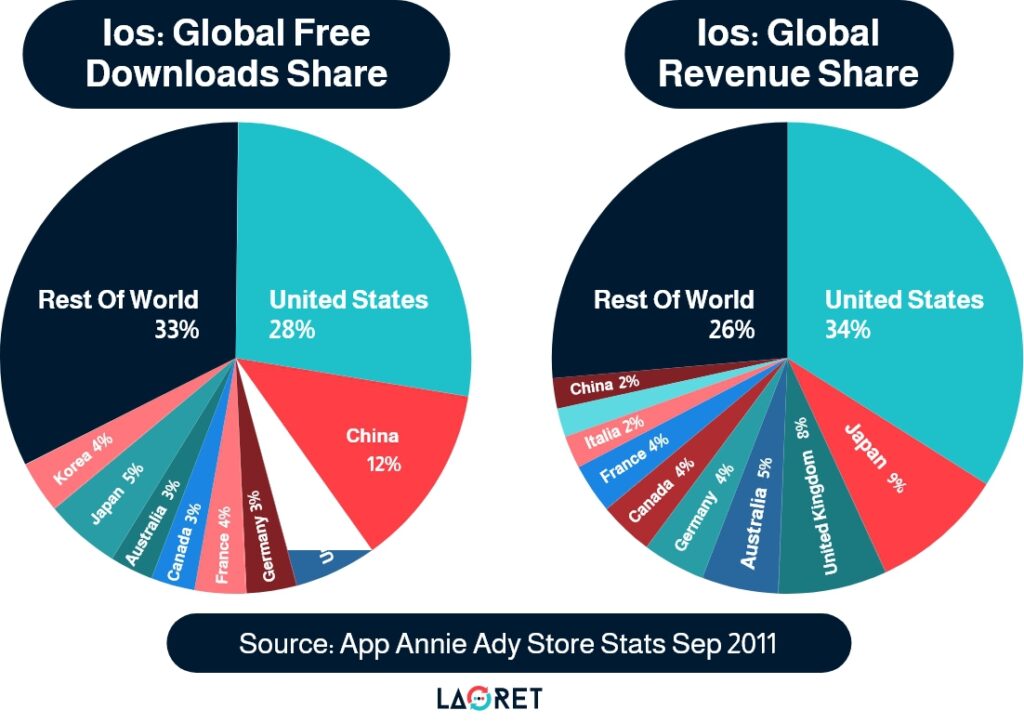
If you want to gain traction in these markets, you’ll have to do what the top 25 games in Asian and European countries do: step up your localization game.
But how much localization is enough?
While translating your app in the store listings is a great place to start, app translation involves more than just translating words; it involves cultural adaptation to ensure the app resonates with local users.
6. Opportunity for User-Generated Content and Feedback
User-generated content is the key to getting authentic marketing material from customers, allowing other customers to see genuine reviews before making a decision. Before installing an app, users first scan the description, scroll through a few screenshots to see some features, and then head to the reviews. Localization works wonders in this aspect because, by localizing your app, you increase user engagement. Consequently, this encourages users to leave positive reviews and create content, resulting in more genuine marketing for your mobile app. This, in turn, helps users become more attracted to your app and increases downloads and revenue.It’s worth mentioning the impressive efforts of Tripadvisor, which enables users to add reviews as well as videos and photos.
Tripadvisor is now available in 28 languages. It even supports dialects of different languages, including Spanish, English, Arabic, and French. No wonder it’s one of the best travel mobile apps in the world, generating great organic interactions and traffic.
With proper localization, your users will lead the dialogue surrounding your mobile app, providing you with insights on what needs improvement and what features to prioritize for promotion.
7. Meeting Local Regulations
When it comes to entering new markets, meeting local regulations is a crucial aspect that businesses must consider.
China, in particular, has some of the most stringent regulations that foreign companies must comply with. The Great Firewall of China, a term coined to describe the country’s internet censorship policies, can make it extremely challenging for businesses to penetrate the market. Despite the challenges, app developers should make an effort to enter the Chinese market due to its potential for high returns. In fact, 92% of the most popular iPhone apps in China are in Chinese, demonstrating the importance of localization for success in the Chinese market.

Don’t miss out on
this essential guide
to ensure your mobile app becomes a worldwide hit.
However, it’s essential to note that China is not the only country with strict regulations. Many countries have their own unique sets of laws and requirements that companies must adhere to. Failure to do so can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines or even legal action.
Another two markets that are also very lucrative are India and Russia, and when it comes to data localization laws, they require the personal data of citizens to be stored on servers located within the country.
Having a native team for your mobile app localization can ensure compliance with local regulatory laws and cultural sensitivities, providing a smooth user experience and avoiding potential legal issues that may arise from non-compliance.
Mobile App Localization for Your App Growth: A Fact Sheet
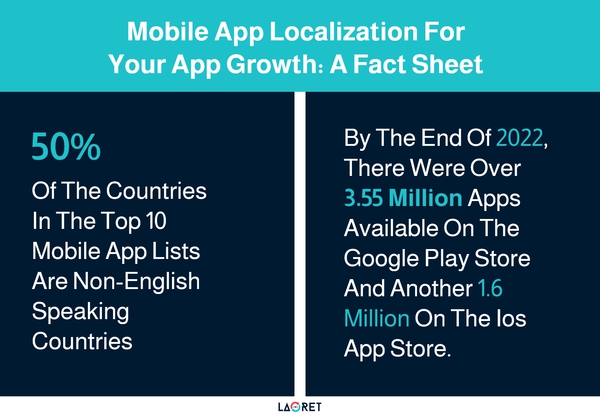
- 50% of the countries in the top 10 mobile app lists are non-English speaking countries (App Annie)
- By the end of 2022, there were over 3.55 million apps available on the Google Play Store and another 1.6 million on the iOS App Store. (Statista) to be represented with two vertical graphs
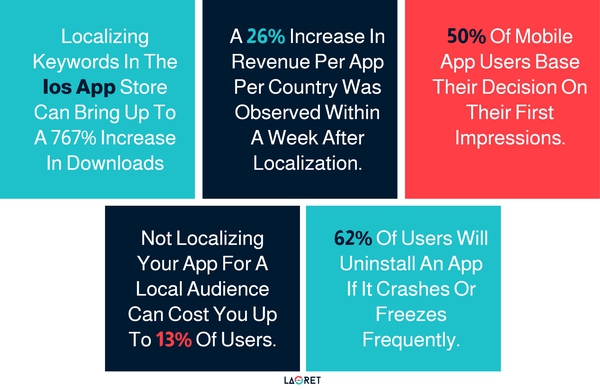
- Localizing keywords in the iOS App Store can bring up to a 767% increase in downloads
- A 26% increase in revenue per app per country was observed within a week after localization. (Appinventiv)
- 50% of mobile app users base their decision on their first impressions. (Storemaven)
- Not localizing your app for a local audience can cost you up to 13% of users. (Appinventiv)
- 62% of users will uninstall an app if it crashes or freezes frequently. (Zippia)
Reach Worldwide Customers: Laoret Mobile App Localization Services
There is a strong appetite for mobile app localization globally, and all surveys and case studies show that it can significantly increase downloads and revenue in target markets. Investing in mobile app localization services can help mobile app developers connect with local audiences, build trust, and improve the overall user experience. At Laoret, we understand the importance but also the complexity of navigating cultural differences. That’s why our team of native experts is here to adapt your mobile app to new markets while ensuring compliance with all relevant regulations. With our expertise in mobile app localization, you’ll rest assured that local audiences will love your product. Request a quote now.






